What Is the :nth-child() CSS Selector?
:nth-child() selects one or more child elements among their direct siblings regardless of node types.
Syntax of the CSS :nth-child() Selector
Section titled “Syntax of the CSS :nth-child() Selector”:nth-child() accepts one argument only. Here is the syntax:
html-element:nth-child(value) { style declarations}The value argument can be one of the following:
- A number: For instance, using
3represents the third child. - The keyword
evenorodd: We use it to represent even or odd children. - The formula
An+B: We use it to express a series of numbers. For instance,2n+3expresses these numbers:[(2x0)+3],[(2x1)+3],[(2x2)+3],[(2x3)+3], and so on.
Note the following:
:nth-child()is a CSS pseudo-class selector.- The
:nth-child()selector works on direct siblings only. - In the
An+Bformula,
Examples of the CSS :nth-child() Selector
Section titled “Examples of the CSS :nth-child() Selector”Below are examples of how to use the CSS :nth-child() pseudo-class selector.
Apply DeepPink to the <p> node that is its parent’s third child
Section titled “Apply DeepPink to the <p> node that is its parent’s third child”The :nth-child() selector below selects the <p> element that is its parent’s third child.
p:nth-child(3) { color: DeepPink;}Suppose the snippet below is the HTML document for the above CSS ruleset. Browsers will apply DeepPink to the second <p> element only.
<h1>First heading 1 element</h1><p>First paragraph element</p><p>Second paragraph element</p><h2>First heading 2 element</h2><p>Third paragraph element</p><h3>First heading 3 element</h3><p>Fourth paragraph element</p><p>Fifth paragraph element</p>The :nth-child() selector works on direct siblings only. For instance, suppose you re-write the HTML snippet above to include nested elements as follows:
<article> <h1>Article's first heading 1 element</h1> <p>Article's first paragraph element</p> <h2>Article's first heading 2 element</h2> <p>Article's second paragraph element</p> <section> <h3>Article's first heading 3 element</h3> <p>Article's third paragraph element</p> <p>Article's fourth paragraph element</p> </section> <h2>Article's second heading 2 element</h2> <p>Article's fifth paragraph element</p> <p>Article's sixth paragraph element</p></article>The p:nth-child(3) selector will apply DeepPink only to the fourth <p> node because it is the third child of its parent.
Apply DeepPink to every odd child that is a <p> node
Section titled “Apply DeepPink to every odd child that is a <p> node”The :nth-child() selector below selects every odd child element that is a <p> node.
p:nth-child(odd) { color: DeepPink;}Assuming the snippet below is the HTML document for the above CSS ruleset, browsers will apply DeepPink to the fourth <p> element only.
<h1>First heading 1 element</h1><p>First paragraph element</p><h2>First heading 2 element</h2><p>Second paragraph element</p><h3>First heading 3 element</h3><p>Third paragraph element</p><p>Fourth paragraph element</p>Apply DeepPink to every even child that is a <p> node
Section titled “Apply DeepPink to every even child that is a <p> node”The :nth-child() selector below selects every even child element that is a <p> node.
p:nth-child(even) { color: DeepPink;}Assuming the snippet below is the HTML document for the above CSS ruleset, browsers will apply DeepPink to the first, second, fourth, and sixth <p> elements.
<article> <h1>Article's first heading 1 element</h1> <p>Article's first paragraph element</p> <h2>Article's first heading 2 element</h2> <p>Article's second paragraph element</p> <p>Article's third paragraph element</p> <section> <h3>Article's first heading 3 element</h3> <p>Article's fourth paragraph element</p> <p>Article's fifth paragraph element</p> </section> <h2>Article's second heading 2 element</h2> <p>Article's sixth paragraph element</p> <p>Article's seventh paragraph element</p></article>Apply DeepPink to the third child element, seventh, eleventh and so on that is a <p> node
Section titled “Apply DeepPink to the third child element, seventh, eleventh and so on that is a <p> node”The :nth-child() selector below selects every <p> child element whose index is a multiple of two (2) with an offset of three (+3).
p:nth-child(2n + 3) { color: DeepPink;}Fun Quiz: If the snippet below is the HTML document for the above CSS ruleset, which elements will the browser style?
<p>First paragraph element</p><p>Second paragraph element</p><p>Third paragraph element</p><p>Fourth paragraph element</p><div><p>Fifth paragraph element</p></div><p>Sixth paragraph element</p><p>Seventh paragraph element</p><p>Eight paragraph element</p><div><p>Nineth paragraph element</p></div><p>Tenth paragraph element</p><p>Eleventh paragraph element</p><p>Twelfth paragraph element</p>Apply DeepPink to the first child, third, fifth, and so on that is a <p> node
Section titled “Apply DeepPink to the first child, third, fifth, and so on that is a <p> node”The :nth-child() selector below selects every <p> child element whose index is a multiple of two (2) with an offset of negative three (-3).
p:nth-child(2n-3) { color: DeepPink;}Fun Quiz: If the snippet below is the HTML document for the above CSS ruleset, which elements will the browser style?
<p>First paragraph element</p><p>Second paragraph element</p><p>Third paragraph element</p><p>Fourth paragraph element</p><div><p>Fifth paragraph element</p></div><p>Sixth paragraph element</p><p>Seventh paragraph element</p><p>Eight paragraph element</p><div><p>Nineth paragraph element</p></div><p>Tenth paragraph element</p><p>Eleventh paragraph element</p><p>Twelfth paragraph element</p>Apply DeepPink to the <p> nodes that are one of the first three children of their parent
Section titled “Apply DeepPink to the <p> nodes that are one of the first three children of their parent”The :nth-child() selector below applies DeepPink to the <p> nodes that are one of their parent’s first three elements.
p:nth-child(-n + 3) { color: DeepPink;}Fun Quiz: If the snippet below is the HTML document for the above CSS ruleset, which elements will the browser style?
<article> <h1>Article's first heading 1 element</h1> <p>Article's first paragraph element</p> <h2>Article's first heading 2 element</h2> <p>Article's second paragraph element</p> <p>Article's third paragraph element</p> <section> <h3>Article's first heading 3 element</h3> <p>Article's fourth paragraph element</p> <p>Article's fifth paragraph element</p> </section> <h2>Article's second heading 2 element</h2> <p>Article's sixth paragraph element</p> <p>Article's seventh paragraph element</p></article>:nth-child() vs. :nth-of-type() – What’s the Difference?
Section titled “:nth-child() vs. :nth-of-type() – What’s the Difference?”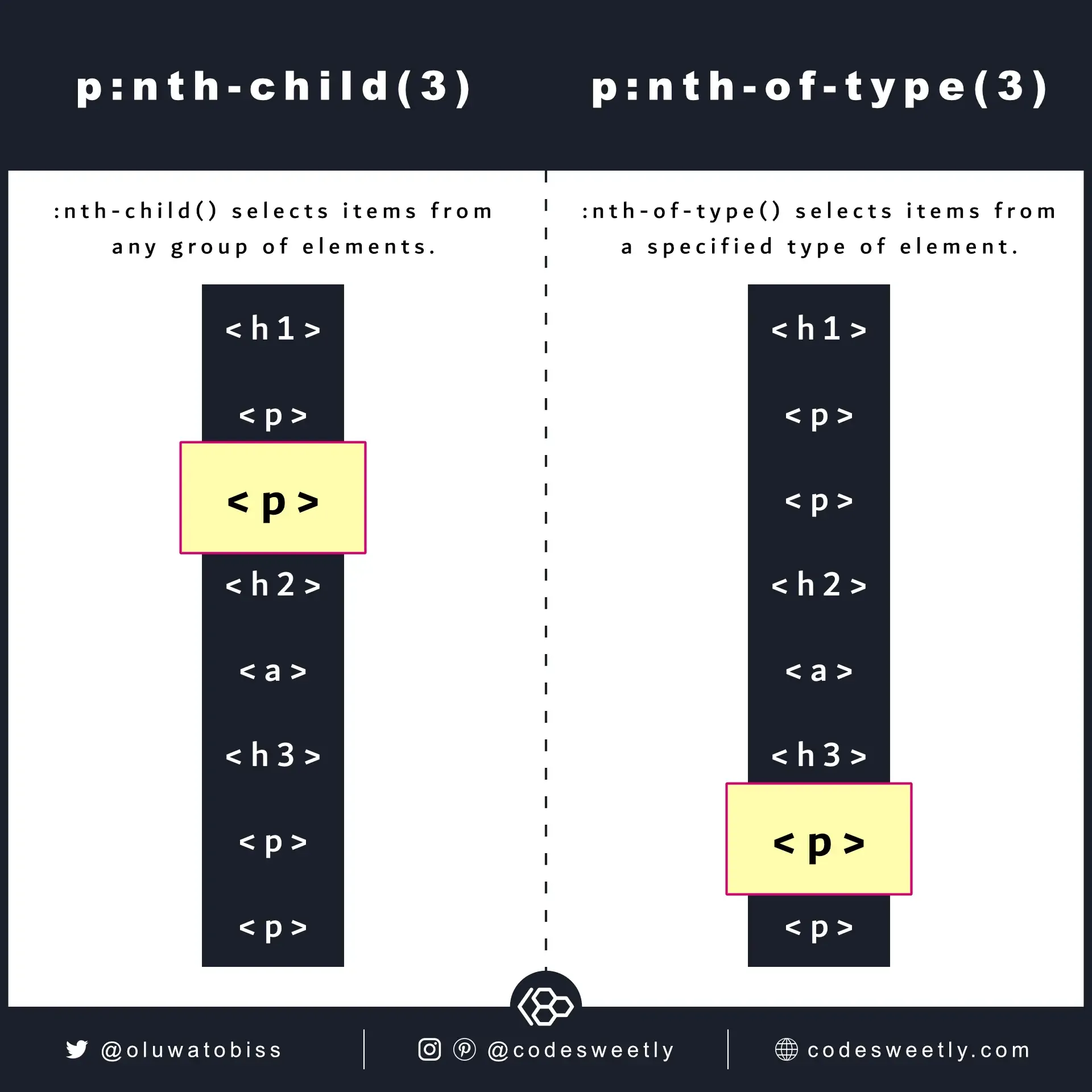
nth-child selects its items from any group of elements. nth-of-type
selects its items from a specified type of element.
:nth-child() selects items from a general group of elements. For instance, selecting a <p> node from a mixed group that includes <h1>, <div>, and <section>.
:nth-of-type() selects items from a specified group of elements. For instance, selecting a <p> node from a group of <p> siblings.